Projects
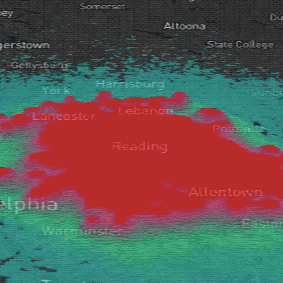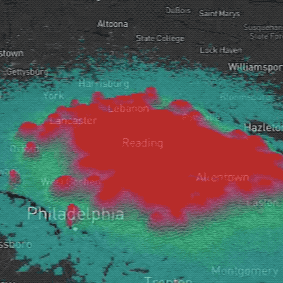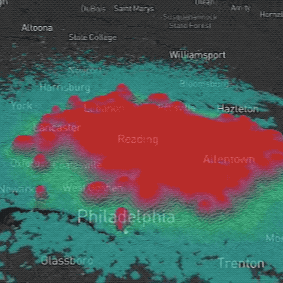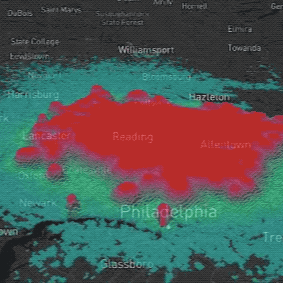
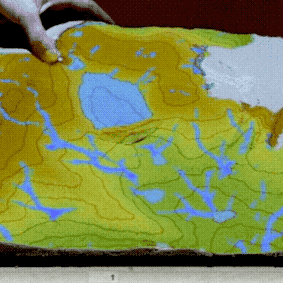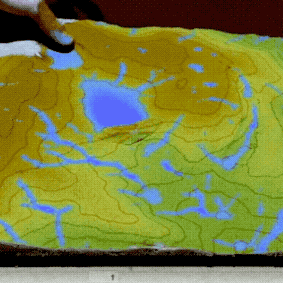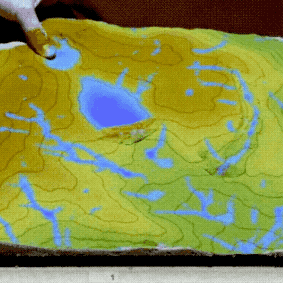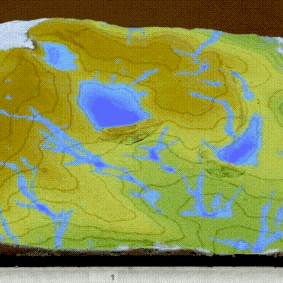
PoPS Model
Geospatial Web Framework & Dashboard
Helps policy makers, land managers, and researchers predict and manage spreading plant disease.
E-Motion
Web-mapping Application
Uses location-based physiological data recorded by wearable sensors from cyclists to help inform urban design decisions.
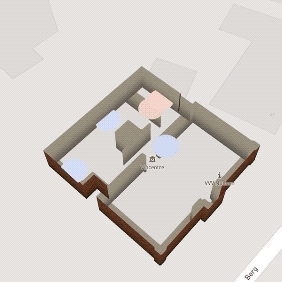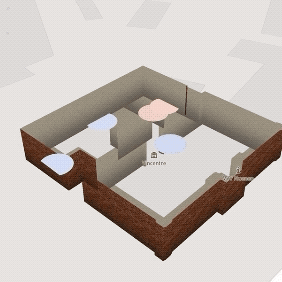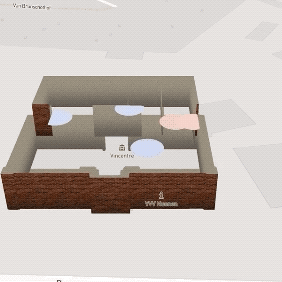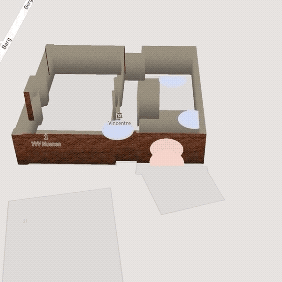
Emotion Museum
Web-mapping Application
Uses location-based physiological data recorded by wearable sensors to help museum directors design exciting museums.
Selected Publications

Space-time Analytics of Human Physiology for Urban Planning
Millar, G. C., Mitas O., Boode W., Hoeke L., de Kruijff J., Mitasova H.
Recent advancements in mobile-sensing technologies like smart watches create new opportunities to improve our understanding of how people experience their environment. Currently, an important urban design issue is the adaptation of infrastructure to increasing cycle and e-bike use. Using data collected from 12 cyclists on a cycling highway between two municipalities in The Netherlands, this paper presents a methodological framework for quantifying and analyzing spatio-temporal variations of emotion and their association with surrounding environmental features. The presented methodological framework, spatial-emotional analyses, and findings from qualitative-quantitative triangulation provide new opportunities for spatial, data-driven approaches to portable-sensing and urban-planning research. Furthermore, our findings have implications for design of infrastructure to optimize cycling experiences.

Tangible Landscape: A Hands-on Method for Teaching Terrain Analysis
Millar, G. C., Tabrizian P., Petrasova A., Petras V., Harmon B., Mitasova H., Meetenmeyer R.
This paper presents novel and effective methods for teaching about topography--or shape of terrain--and assessing 3-dimensional spatial learning using tangibles. We used Tangible Landscape--a tangible interface for geospatial modeling--to teach multiple hands-on tangible lessons on the concepts of grading, geomorphology, and hydrology. We examined students' ratings of the system's usability and user experience and tested students' acquisition and transfer of knowledge. Our results suggest the physicality of the objects enabled the participants to effectively interact with the system and each other, positively impacting ratings of usability and task-specific knowledge building. These findings can potentially advance the design and implementation of tangible teaching methods for the topics of geography, design, architecture, and engineering.

Creating Content Guidelines for Consistent Display of Information on an Ecommerce Website
Pryor, M., Millar, G. C., McNamara, A., Kaufman, L., & McLaughlin, A.C.
As part of a project in collaboration with Lenovo's Global UX team, we analyzed a website using heuristic analysis, a cognitive walkthrough, and feedback from users through verbal protocols. With this information, we created a prototype version of proposed content guidelines. These guidelines aim to improve consistency on the website, which allowed users to quickly compare multiple laptops as well as make connections between the laptop hardware and typical uses. In this paper, we describe our process behind developing these guidelines and the resulting guidelines themselves to show how researchers may develop their own guidelines.
Book Chapters

Using Data Visualizations to Foster Emotion Regulation During Self-Regulated Learning with Advanced Learning Technologies
Azevedo, R., Taub, M., Mudrick, N. V., Millar, G. C., Bradbury, A. E., & Price, M. J.
We present a theoretically-based and empirically-driven conceptual framework that addresses emotion regulation by proposing the use of visualizations of one's and others' CAMM-SRL multichannel data to facilitate learners' monitoring and regulation of their emotions during learning with advanced learning technologies. We conclude with future directions that can lead to a systematic interdisciplinary research agenda that addresses outstanding emotion regulation-related issues by integrating models, theories, methods, and analytical techniques for the areas of cognitive, learning, and affective sciences, human computer interaction, data visualization, big data, data mining, data science, learning analytics, open learner models, and SRL.